[ad_1]
Banks around the globe are charging on with their sustainability efforts, regardless of taking a major monetary hit from the Covid-19 disaster. A brand new Mazars report evaluates the worldwide banking sector alongside varied inexperienced metrics.
The pandemic-induced financial disaster flattened rates of interest, dampened spending and pushed credit score losses by way of the roof – all of which is ready to value the worldwide banking sector trillions of dollars within the close to future.
Mazars studied sustainability and reporting practices at 37 banks throughout North America, Europe, Asia Pacific and Africa to see how the inexperienced agenda is faring amid these extreme losses. The outcomes present that 2020 and all its landmark occasions have solely intensified the sustainability drive in finance. Mazars accomplice Leila Kamdem-Fotso supplied a proof.

“The monetary world can not see its future as separate from the setting and local weather change developments. In 2020 alone, pure hazards resulted in $210 billion of damages and the Financial institution of England estimates as a lot as $20 trillion of property could possibly be in danger from local weather change.”
Certainly, local weather change and environmental, social and governance (ESG) elements now stand a top the risk agenda, and banks are taking multidimensional motion to adapt in response to Mazars. The agency assessed banks primarily based on the function of sustainability in: tradition & governance, technique, danger administration, disclosure & reporting; and companies & merchandise.
The outcomes are promising throughout the board. Mazars ran the same survey final yr, to search out that lower than half of banks had been fostering a tradition of sustainability and adapting their governance construction accordingly. This yr, the determine stands at just below 75%.

Measures to this finish embody coaching programmes, sustainability insurance policies, and statements from the board on sustainability commitments – every being applied by greater than 80% of banks. And these statements are backed up by concrete sustainability targets the are particular, measurable, achievable, sensible and time-bound (SMART) in 70% of the circumstances.
Most targets are aligned with multilateral aims such because the Sustainable Growth Targets (SDGs) or the Paris Local weather Settlement of 2015. Per the report, properly over half of banks are piloting the Paris Settlement Capital Transition Evaluation (PACTA) – a device that measures the alignment of monetary portfolios with stipulations within the Paris accord.
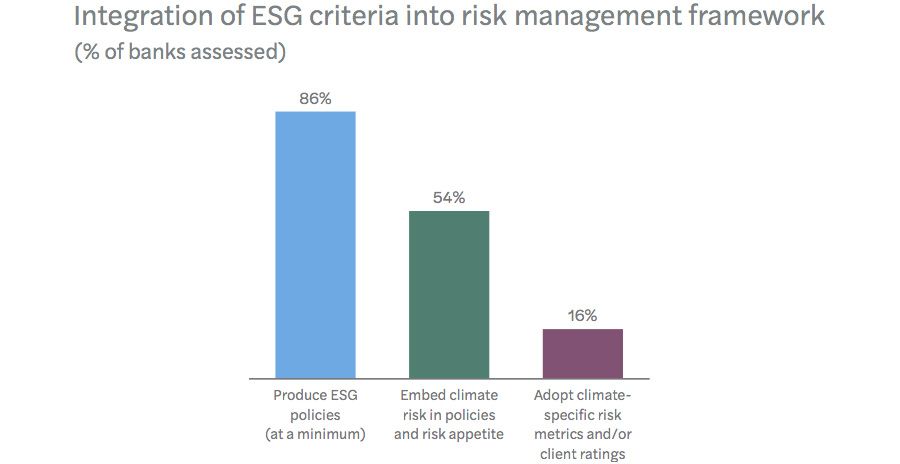
So sustainability efforts are being quantified by way of collaborative frameworks. Sadly, banks are struggling to search out concrete techniques that may measure local weather dangers. Little question about dedication: almost 90% of banks have produced an ESG coverage on the very least, whereas greater than half think about local weather elements in broader danger administration efforts.
But, lower than 1 / 4 can present “quantitative knowledge on the materiality of local weather dangers” in response to the report. This choose group has managed to crystallise clear indicators of environmental and social influence, whereas the remaining wrestle with a scarcity of measurable knowledge.
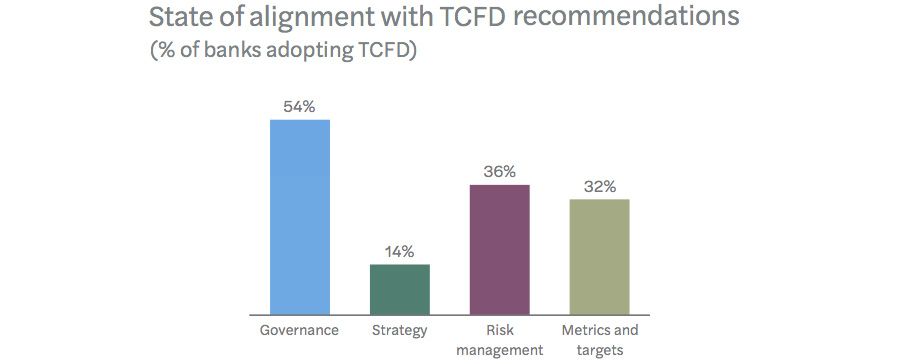
Multilateral efforts have emerged right here too, most notably the Taskforce on Local weather-Associated Monetary Disclosures (TCFD) – a 2016 framework from the Monetary Stability Board that lays out clear metrics on climate-related governance, technique, danger administration and targets. Practically 80% of banks implement TCFD reporting requirements.
That mentioned, few have managed to match its suggestions. Simply over half meet TCFD requirements on governance, whereas round a 3rd are on top of things on danger administration and targets. Technique alignment with TCFD is much more woeful, hovering under 15%.

Final on the checklist of Mazars’ standards is accountable merchandise, the place company choices are excelling however non-public clients nonetheless have few choices. Practically 80% of banks have inexperienced bonds in place for institutional buyers and companies, whereas sustainability bonds and inexperienced loans for people are solely a actuality at lower than 40% of banks.
Regional breakdown
All issues thought of, the Mazars research stretches throughout the globe, and distinct regional variations are seen throughout standards. Sustainable tradition and governance, for example, is most prevalent in France and the UK, adopted by the Americas. Different European international locations, in addition to banks in Africa and APAC lag method behind on this metric.

An analogous breakdown is seen throughout long-term sustainability targets; the presence of local weather and ESG elements in risk-management frameworks; and alignment with ESG reporting requirements. The one exception is Latin America – which tails off in efficiency throughout different metrics, whereas APAC banks do moderately properly alongside ESG-related reporting. Barring Latin America and Africa, properly over 80% of banks throughout all areas now supply accountable companies and merchandise.
The numbers are promising, and Kamden-Fotso positions standardisation as essential to additional progress. “Challenges stay, and our benchmark research reaffirms that robust sustainability practices typically come hand-in-hand with constant business pointers and necessities supplied by native regulators and governments.
[ad_2]
Source link


![WordPress database error: [You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MariaDB server version for the right syntax to use near ‘+thisValue3+ where ID_P=’+thisValue2+” at line 1]SELECT * FROM players_+thisValue3+ where ID_P=’+thisValue2+’Stats Players | Tennis Tonic](https://adidasblog.digitalsnazz.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/1609113710_Facebook-default-75x75.jpg)